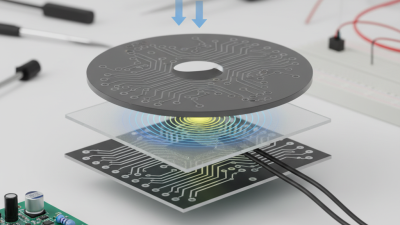
The evolution of electronics has ushered in a new era of efficiency and performance, with conductive materials playing a crucial role in this transformation. One such material, Ito conductive, has garnered significant attention due to its unique properties and versatility. Comprising a combination of indium oxide and tin oxide, Ito conductive materials exhibit exceptional electrical conductivity and optical transparency, making them ideal candidates for various applications in electronic devices, ranging from displays to photovoltaic cells.
As the demand for increasingly sophisticated electronic devices continues to rise, understanding the characteristics and advantages of Ito conductive materials becomes essential. They not only enhance device performance but also contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability in electronics. By delving into the mechanisms that underpin the functionality of Ito conductive, researchers and developers can unlock new possibilities for innovation in the field of electronics.
In this exploration, we will examine the fundamental properties of Ito conductive materials, their applications, and the advancements being made to optimize their performance. By shedding light on these aspects, we aim to illustrate the pivotal role Ito conductive plays in shaping the future of electronics and its contributions to achieving enhanced performance across various technological realms.

Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) is a widely studied conductive material renowned for its unique blend of electrical conductivity and optical transparency. Composed mainly of indium oxide and tin oxide, ITO serves as a crucial component in various electronic applications, including touch screens, solar cells, and flat-panel displays. The properties that make ITO valuable in electronics include its high conductivity, low light absorption, and ability to be deposited in thin films, which is essential for energy-efficient devices.
When considering the integration of ITO into electronics, it’s important to account for its surface properties. ITO’s surface can be modified through various treatment processes to enhance its adhesion properties when applied onto different substrates. This adjustment can significantly impact the overall performance and longevity of electronic devices. Furthermore, the doping levels of tin affect both the conductivity and the optical characteristics of ITO, allowing for tailored performance based on specific application requirements.
Tip: When working with ITO in projects, ensure to maintain cleanliness and a controlled environment during handling and deposition, as contaminants can severely affect the performance of the material. Also, consider exploring alternative conductive materials that can complement or even replace ITO, particularly in applications where flexibility or lower cost is a priority.
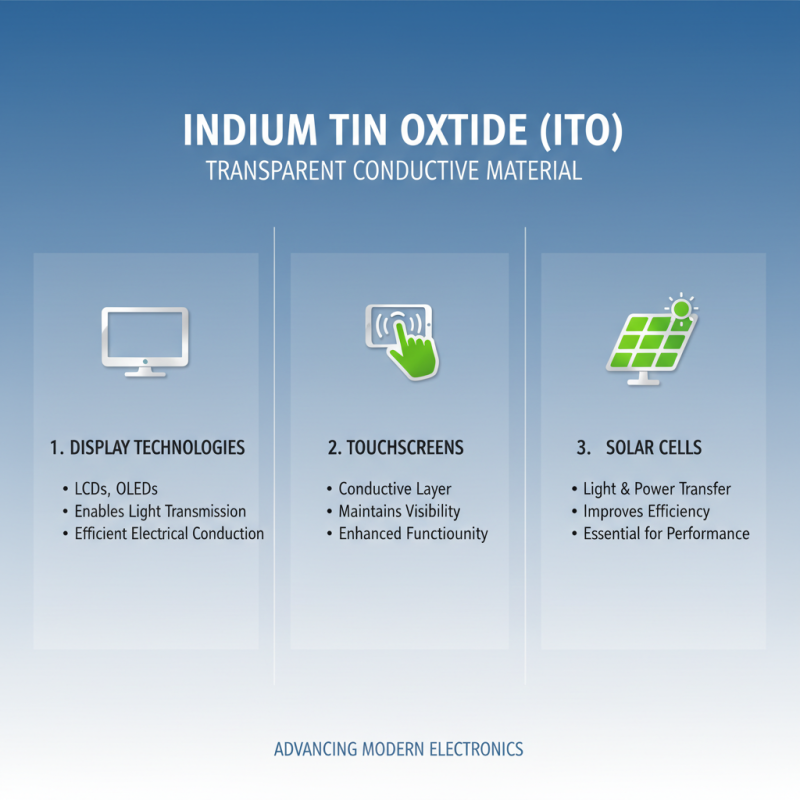
Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) conductive materials play a pivotal role in the advancement of modern electronics. Primarily known for their transparent conductive properties, ITO films are widely utilized in display technologies, including liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). These materials enable the transmission of light while facilitating efficient electrical conduction, thereby enhancing the visual quality and performance of screens. Their ability to provide a conductive layer without obstructing light makes them invaluable for touchscreens and solar cells, where both visibility and functionality are essential.
Beyond displays, ITO conductive materials are also finding applications in emerging technologies such as flexible electronics and smart textiles. Their compatibility with various substrates allows for the development of lightweight, bendable devices that can be integrated into clothing and other everyday items. This versatility opens new avenues for wearable technology, allowing for seamless integration of electronic components into fabrics. Furthermore, ITO is being explored in energy harvesting systems, where its conductive properties are leveraged to create efficient, thin-film solar panels that can be used in various environments, significantly contributing to the sustainability of electronic devices.
Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) materials are becoming increasingly significant in the realm of electronics due to their unique properties that enhance device performance. One of the primary advantages of ITO is its excellent electrical conductivity coupled with high optical transparency, making it a preferred choice for applications such as touchscreens, LCDs, and other optoelectronic devices. By utilizing ITO materials, manufacturers can produce lighter, thinner, and more efficient devices without compromising on performance.
Tips: When designing electronic devices, consider opting for ITO for components that require both conductivity and transparency. This can lead to significant improvements in device efficiency and user experience. Additionally, integrating ITO materials can help reduce energy consumption, leveraging their conductive properties to enhance power management in electronics.
Moreover, ITO's environmental stability and resistance to corrosion further boost its appeal in electronics, ensuring longevity and reliability. These attributes contribute to maintaining performance over time, which is especially crucial for consumer electronics that are subjected to daily use. With the push for more sustainable and efficient technology, ITO materials offer a viable solution for meeting modern electronics' demands.
Tips: Regularly evaluate the performance of electronic devices that incorporate ITO materials, as this can provide insights into enhancing future designs. Staying informed about advancements in material science can also enable the adoption of the latest innovations for better performance outcomes.
Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) has long been a go-to material for transparent conductive applications in electronics, particularly in touchscreens and displays. However, several challenges and limitations hinder its widespread adoption and optimization. One primary concern is the brittleness of ITO, which can lead to cracking and ultimately failure in flexible electronics. This fragility makes it unsuitable for certain applications where mechanical flexibility is critical, as it cannot withstand repeated bending or stretching without compromising performance.
Additionally, the production of ITO involves the use of indium, a rare and expensive element. The scarcity of indium raises economic and supply chain issues, potentially leading to increased costs and sustainability concerns. The extraction process of indium also poses environmental challenges, contributing to the overall difficulty in scaling ITO-based technologies.
Moreover, the electrical properties of ITO can degrade over time due to exposure to moisture and oxygen, which poses reliability concerns for long-term applications. These limitations necessitate ongoing research to find alternative materials or methods that can enhance performance while mitigating the drawbacks associated with ITO.
The research and development of indium tin oxide (ITO) conductive materials are evolving rapidly, driven by the demand for high-performance electronics across various industries. Recent reports estimate that the global ITO market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8%, reaching approximately USD 2.7 billion by 2025. This growth is primarily fueled by the increasing adoption of ITO in applications like touch screens, flat panel displays, and solar cells, highlighting its crucial role in enhancing electronic device functionality.
Future trends in ITO conductive material research indicate a strong focus on improving the material's transparency and electrical conductivity. Researchers are exploring novel approaches such as doping with alternative elements and developing hybrid materials that combine ITO with other conductive compounds. According to a 2022 industry analysis, these advancements could potentially reduce costs by up to 20% while maintaining high performance, thereby making ITO more accessible for a wider range of applications. Furthermore, environmentally friendly and sustainable production methods are becoming vital, as companies seek to minimize their ecological footprint while meeting the rising global demand for electronic devices.